Index
Introduction
Creating a radar system is a fascinating project that brings together various electronic components to build a functional and visually engaging device. In this guide, we’ll demonstrate how to use an Arduino Uno, a sonar sensor, a servo motor, and a TFT display to build your own radar system. Follow along to integrate these components and see how they work together to create a radar-like experience.
This radar system project demonstrates how to integrate a sonar sensor, servo motor, and TFT display with an Arduino Uno to create a functional radar-like device. It’s a great way to learn about sensor integration, motor control, and display interfacing. Customize and expand on this project to suit your needs and enjoy the process of creating your own radar system!
Required Components
- Arduino UNO / Nano
- Sonar sensor
- Servo Motor
- TFT Display
- Jumper Wires
- Breadboard
- Power supply
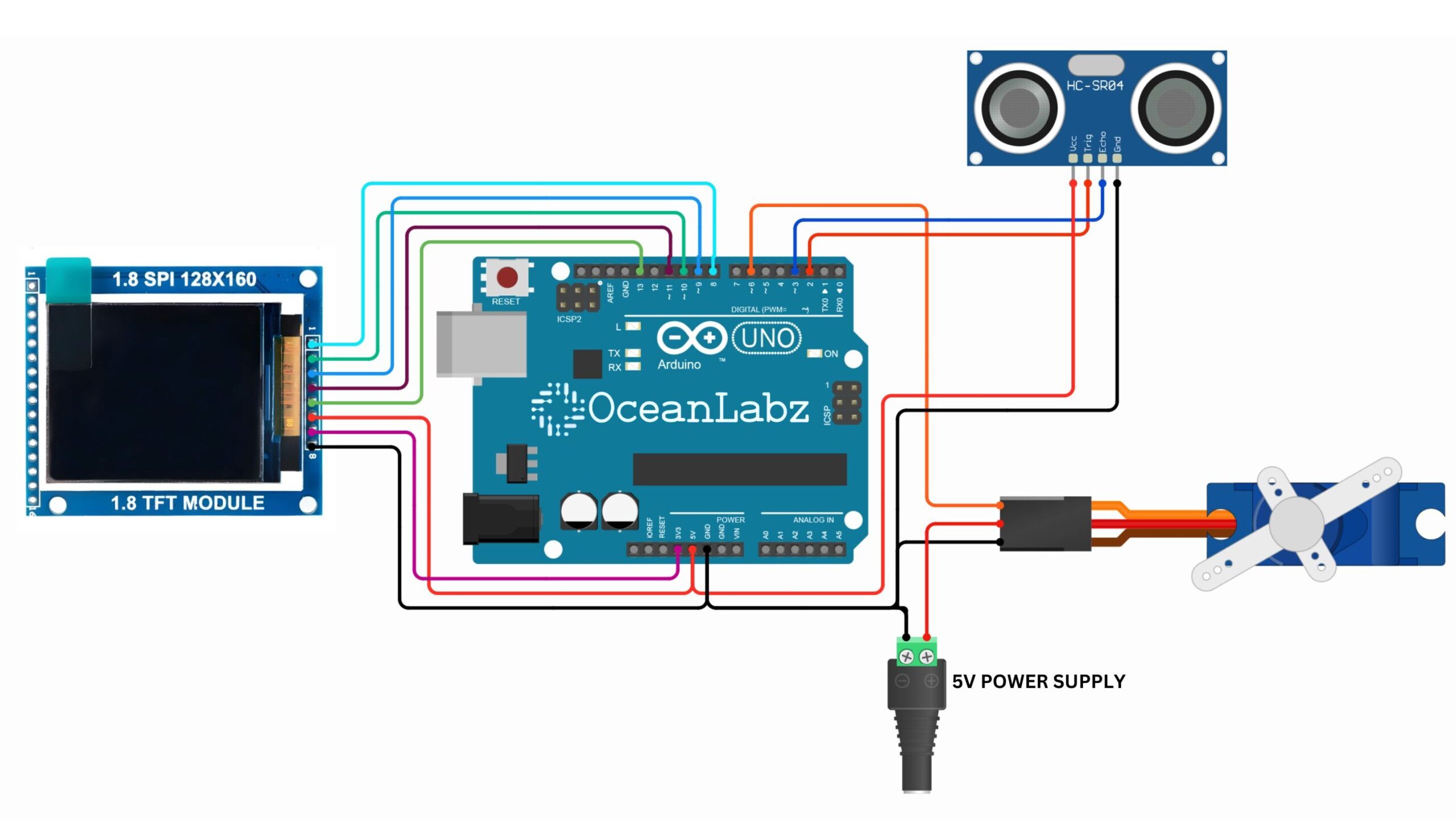
Circuit Diagram / Wiring
- Sonar sensor with Arduino
- Sonar VCC → 5V (Arduino)
- Sonar GND → GND (Arduino)
- Sonar TRIG → Pin 2 (Arduino)
- Sonar ECHO→ Pin 3 (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly with Arduino
- TFT Dispaly VCC → 5V (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly GND → GND (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly BL→ Pin 3V (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly CLK→ Pin 13 (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly DIN→ 11 (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly DC→ 9 (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly CS→ Pin 10 (Arduino)
- TFT Dispaly RST→ Pin 8 (Arduino)
- Servo Motor with Arduino
- Servo Motor VCC → (Positive terminal of 5-6V external power.)
- Servo Motor GND → Common GND (Arduino GND + external power GND)
- Servo Motor SDA → Pin 6 (Arduino)
Arduino Code / Programming
Make sure you have the required libraries installed:
- Servo library for Servo motor.
#include <Servo.h>
#include <TFT.h> // Arduino LCD library
#include <SPI.h>
// Pin definitions
#define cs 10
#define dc 9
#define rst 8
Servo servo;
TFT TFTscreen = TFT(cs, dc, rst);
int interval = 0;
double distance = 0;
char rc_Printout[4];
void setup() {
servo.attach(6); // Servo signal pin
pinMode(2, OUTPUT); // Trig pin
pinMode(3, INPUT); // Echo pin
Serial.begin(9600);
TFTscreen.begin();
TFTscreen.background(0, 0, 0);
}
void loop() {
int r_beam = 100; // Beam radius
TFTscreen.stroke(255, 255, 255);
TFTscreen.circle(80, 128, r_beam + 2);
TFTscreen.setTextSize(2);
TFTscreen.text("Dist(cm)", 0, 0);
// Right rotation
for (int i = 0; i < 180; i++) {
servo.write(i);
measure_dist();
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("\n");
delay(20);
int r = distance * 2;
String r_Printout = String(r / 2);
TFTscreen.stroke(0, 0, 0);
TFTscreen.setTextSize(2);
TFTscreen.text(rc_Printout, 100, 0);
r_Printout.toCharArray(rc_Printout, 4);
TFTscreen.stroke(255, 255, 255);
TFTscreen.setTextSize(2);
TFTscreen.text(rc_Printout, 100, 0);
TFTscreen.stroke(70, 70, 70);
TFTscreen.line(80, 128, 80 + r_beam * cos((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180), 128 + r_beam * sin((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180));
TFTscreen.stroke(0, 255, 0);
TFTscreen.circle(80 + r * cos((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180), 128 + r * sin((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180), 2);
}
TFTscreen.background(0, 0, 0);
TFTscreen.stroke(255, 255, 255);
TFTscreen.circle(80, 128, r_beam + 2);
TFTscreen.setTextSize(2);
TFTscreen.text("Dist(cm)", 0, 0);
// Left rotation
for (int i = 180; i > 0; i--) {
servo.write(i);
measure_dist();
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("\n");
delay(20);
int r = distance * 2;
String r_Printout = String(r / 2);
TFTscreen.stroke(0, 0, 0);
TFTscreen.setTextSize(2);
TFTscreen.text(rc_Printout, 100, 0);
r_Printout.toCharArray(rc_Printout, 4);
TFTscreen.stroke(255, 255, 255);
TFTscreen.setTextSize(2);
TFTscreen.text(rc_Printout, 100, 0);
TFTscreen.stroke(70, 70, 70);
TFTscreen.line(80, 128, 80 + r_beam * cos((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180), 128 + r_beam * sin((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180));
TFTscreen.stroke(0, 255, 0);
TFTscreen.circle(80 + r * cos((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180), 128 + r * sin((360 - i) * 3.14 / 180), 2);
}
TFTscreen.background(0, 0, 0);
}
void measure_dist() {
Serial.read();
// Pulse
digitalWrite(2, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(100);
digitalWrite(2, LOW);
// Measure the interval
interval = pulseIn(3, HIGH);
distance = interval * 0.017; // cm
Serial.print(interval, DEC);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(distance, 1);
Serial.print("\n");
}
Explanation
- The code uses a servo motor and ultrasonic sensor to measure distances while rotating the servo from 0° to 180° and back.
- A TFT display visually plots the measured distance and updates it dynamically.
- The
measure_distfunction calculates the distance using the ultrasonic sensor’s pulse duration. - Servo movement, distance calculation, and real-time display updates are synchronized in a continuous loop.