Index
Introduction
The nRF24L01 is a popular wireless transceiver module designed for low-power, short-range communication. It operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band, making it suitable for a variety of wireless communication applications.
Hardware Overview
Working Principle
The nRF24L01 works by using the 2.4 GHz ISM band for wireless communication. It interfaces with a microcontroller via SPI, sending and receiving data packets at up to 2 Mbps. The module uses the Enhanced ShockBurst protocol to handle automatic packet acknowledgment and retransmission, ensuring reliable communication. It supports up to six data pipes for simultaneous multi-point communication. Power-saving modes are included to optimize battery life, and the module can operate up to 100 meters in open space with its standard antenna.
Application
- Remote controls
- Wireless sensor networks
- Data transmission between devices
- IoT devices
- Gaming controllers
- Home automation systems
Technical Specification
- Type: NRF24L01 Wireless Transceiver Module
- Function: Enables wireless communication with Arduino
- Compatibility: Designed for Arduino boards
- Communication Protocol: NRF24L01 radio transceiver chip
- Range: Several meters to a few hundred meters
- Frequency: 2.4GHz ISM band
- Data Rate: Configurable
- Applications: Remote control, sensor networks, IoT
- Integration: Easily integrates into Arduino projects
Pinout
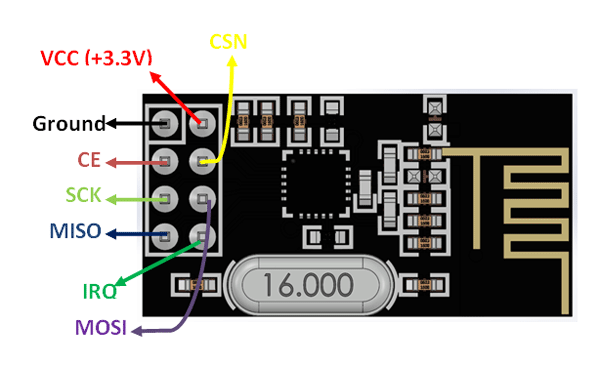
- GND: Ground
- VCC: Power supply (1.9V to 3.6V, typically 3.3V)
- CE: Chip Enable, activates RX or TX mode
- CSN: Chip Select Not, SPI chip select (active low)
- SCK: Serial Clock, SPI clock
- MOSI: Master Out Slave In, SPI data input
- MISO: Master In Slave Out, SPI data output
- IRQ: Interrupt Request, optional interrupt pin
Circuit Description
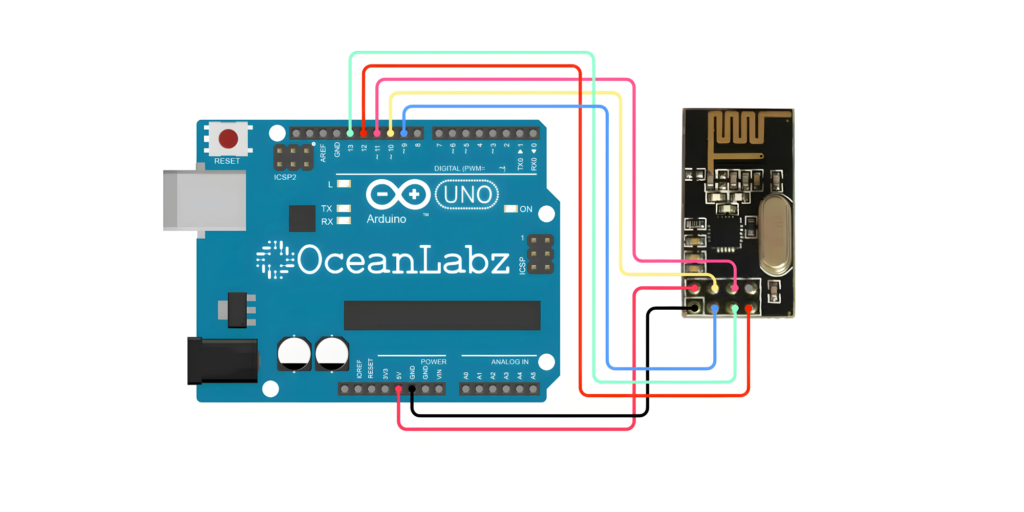
| nRF24L01 Pin | Arduino Pin |
| VCC | 3.3 V |
| GND | GND |
| CE | D9 |
| CSN | D10 |
| SCK | D13 |
| MOSI | D11 |
| MISO | D12 |
Circuit Diagram
Code
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
// Set up the radio object
RF24 radio(9, 10); // CE, CSN
// Address for the nodes
const byte address[6] = "00001";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
radio.begin();
radio.openWritingPipe(address);
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MIN);
radio.stopListening();
}
void loop() {
const char text[] = "Hello, World!";
radio.write(&text, sizeof(text));
Serial.println("Sent: Hello, World!");
delay(1000);
}


